Introduction to the Maplab Framework
Terminology
- Mapping: The process in which the robot builds a model of the environment by fusing the output from one or multiple sensors.
- Missions: A single continuous mapping session for one robot.
- Map: A representation of the environment generated through mapping and used for localization. A map is composed of one or multiple missions combined together.
- Multi-Session Mapping: Collecting data in the same place at different times, and enabling offline operations to and between the different missions.
- Multi-Robot Mapping: Multiple robots simultaneously exploring an environment, with the aim to create one globally consistent map.
- Localization: The process in which the robot infers its position relative wrt. a model of the environment.
- SLAM: Simultaneous Localization and Mapping is the process in which a robot both builds a map in a previously unknown environment, and at the same time localizes in it.
- Landmark A 3D point which was visible from multiple viewpoints, and servers as a reference for the robot's position.
- Loop-Closure: The process of recognizing previously visited places which allows the robot to correct for any error accumulated during exploration of the environment.
- Dense-Reconstruction: The process of building a 3D-model with a high number of points.
Overview
A modern autonomous robotic system is composed of many software building blocks (SLAM, path planning, scene interpretation), most of them depending on some form of localization and mapping. Therefore, there is a need for an API that allows these different elements to communicate, with as little inter-dependency as possible. For this reason in maplab we use ROS to interface between components. However, the internal workings of maplab are written as independent of ROS as possible to promote the easy reuse of the code.
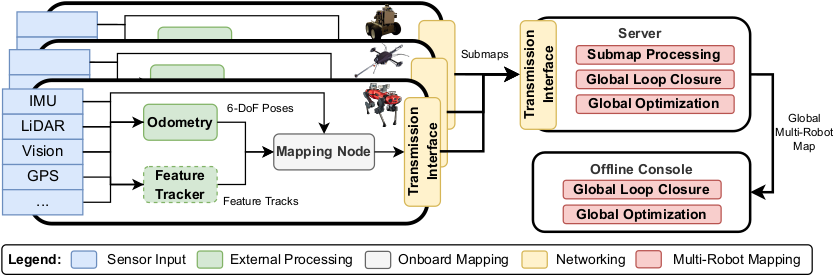
Maplab 2.0 can be divided into three main components:
- Mapping Node: Runs on a robot and takes as input an odometry source and the raw sensor information to create a map.
- Mapping Server: Runs a base station or on one of the robots. It periodically collects maps from one or more robots and merges them together into one globally consistent map.
- Console: The console is meant for offline map optimization and multi-session mapping.
Below is an overview of one possible configuration.