Multi-session use case: CLA, multi-floor use-case
This tutorial will show you how to reproduce the large scale multi-session mapping use-case presented in the paper.
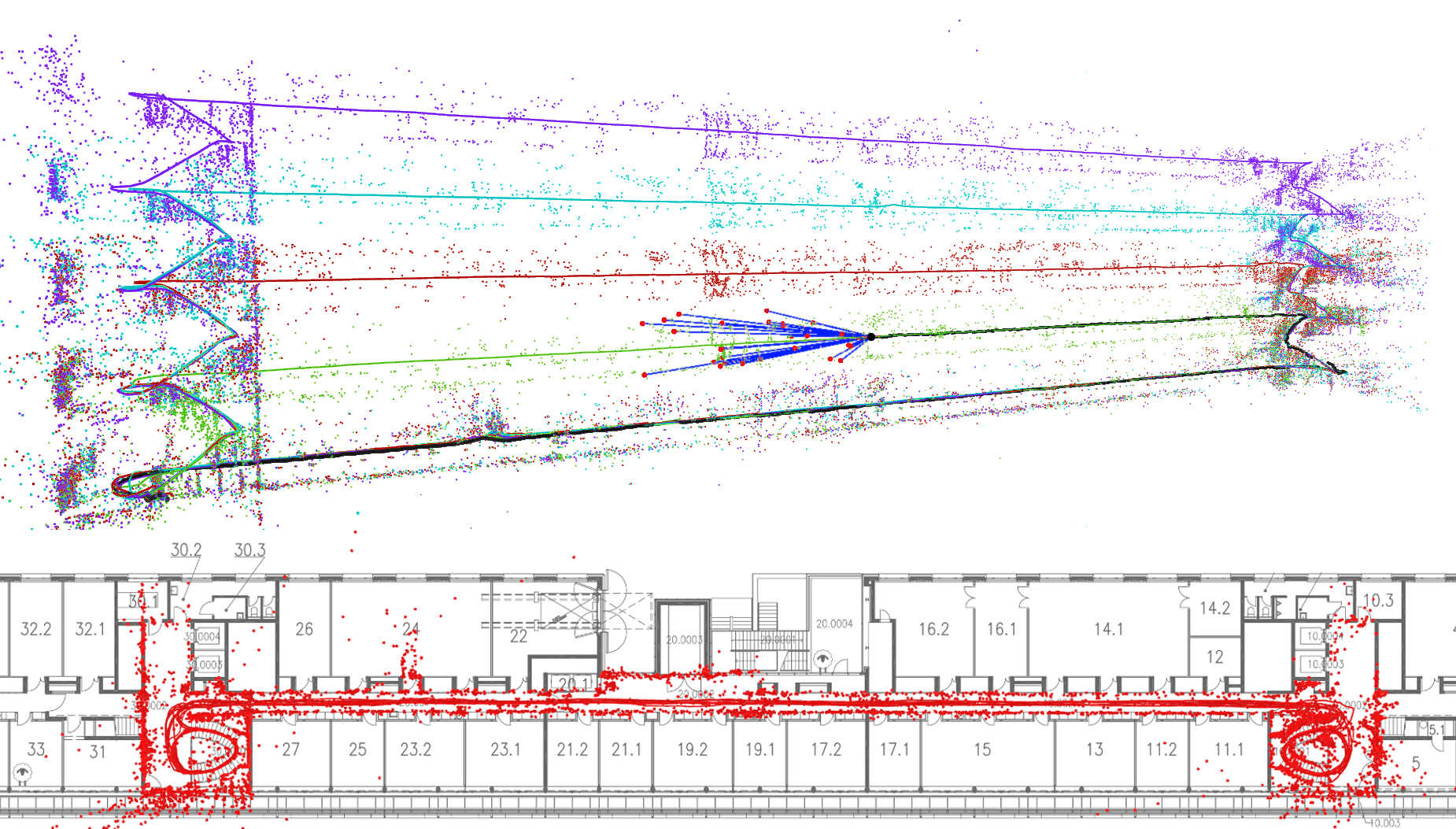
Datasets:
You can download the rosbags and camera/IMU calibration here.
The files you need:
- bags
- cla_floor_f.bag
- cla_floor_g.bag
- cla_floor_h.bag
- cla_floor_j.bag
- cla_floor_f_v2_for_localization.bag
- Intended to be used to test the localization, not to build the localization
- calibration
- imu-adis16488_cla.yaml
- imu-sigmas-rovio_cla.yaml
- imu-adis16488_cla.yaml
Alternatively, you can download the prebuilt maps directly from our dataset page.
Instructions:
Use the [[Running ROVIOLI in VIO mode]] tutorial to create the initial open-loop maps.
Important: Use the camera/imu calibration provided with the dataset.
--ncamera_calibration=ncamera_cla.yaml --imu_parameters_maplab=imu-adis16488_cla.yaml --imu_parameters_rovio=imu-sigmas-rovio_cla.yamlIn order to create the maps, make sure you use these flags:
# We don't need images for this, they will only lead to a large map folder. --map_builder_save_image_as_resources=false # This is not strictly needed, but if set to true, this will create a # localization map version for each map, which depending on the current # implementation of ROVIOLI might include key-framing or summarization, # which we would like to avoid for now. --optimize_map_to_localization_map=falseYou might want to use these flags as well:
# Visualize the ROVIO vio results. --rovio_enable_frame_visualization=true # Increase playback speed 2x. --vio_rosbag_realtime_playback_rate=2.0 # Will overwrite the vi-map if there is already one # stored in the target folder. --overwrite=true # Increase verbosity of ROVIOLI --v=1Check your maps.
After step 1 you should have the following maps/map structure (with whatever names you chose):
<your_dataset_folder_path> ├── cla_f_vi_map │ ├── metadata │ ├── resource_info │ ├── resources │ └── vi_map │ ├── edges │ ├── landmark_index │ ├── missions │ ├── optional_sensor_data │ ├── sensors.yaml │ ├── vertices0 │ ├── vertices1 │ ├── ... │ └── vertices17 ├── cla_g_vi_map │ ├── metadata │ ├── resource_info │ ├── resources │ └── vi_map │ ├── edges │ ├── landmark_index │ ├── missions │ ├── optional_sensor_data │ ├── sensors.yaml │ ├── vertices0 │ ├── ... │ └── vertices22 ├── cla_h_vi_map │ ├── metadata │ ├── resource_info │ ├── resources │ └── vi_map │ ├── edges │ ├── landmark_index │ ├── missions │ ├── optional_sensor_data │ ├── sensors.yaml │ ├── vertices0 │ ├── ... │ └── vertices24 └── cla_j_vi_map ├── metadata ├── resource_info ├── resources └── vi_map ├── edges ├── landmark_index ├── missions ├── optional_sensor_data ├── sensors.yaml ├── vertices0 ├── ... └── vertices28Align, loop-close and optimize maps:
Load all maps, join, align, relax, loop close and optimize them.
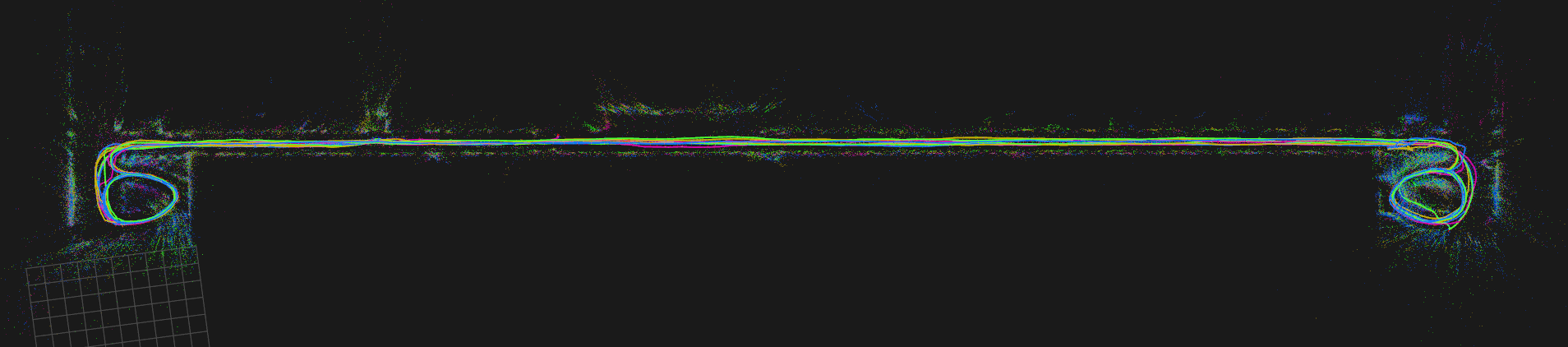
load --map_folder=<your_dataset_folder_path>/cla_f_vi_map load --map_folder=<your_dataset_folder_path>/cla_g_vi_map load --map_folder=<your_dataset_folder_path>/cla_h_vi_map load --map_folder=<your_dataset_folder_path>/cla_j_vi_map # This will create a joint map with 4 missions join_all_maps --target_map_key cla_f_g_h_j_vi_map # Visualize all missions with different colors. v --vis_color_by_missionYou should see the following:
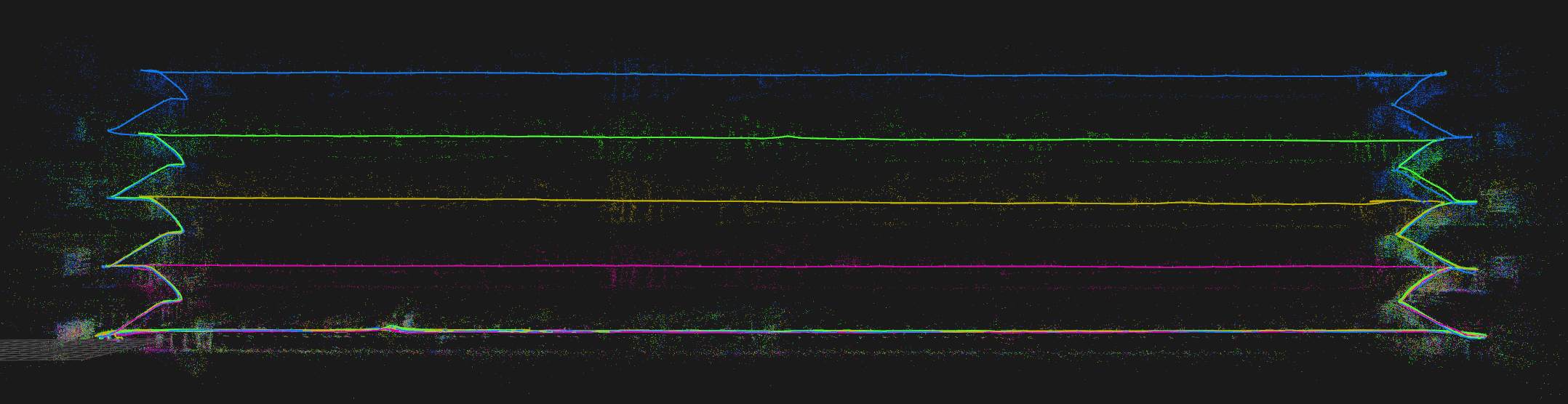
# Set one of the base frames to "known" to be able # to anchor all other maps with respect to that. sbk # Align all missions. aam # Visualize all missions with different colors. v --vis_color_by_missionYour map should now look like this:
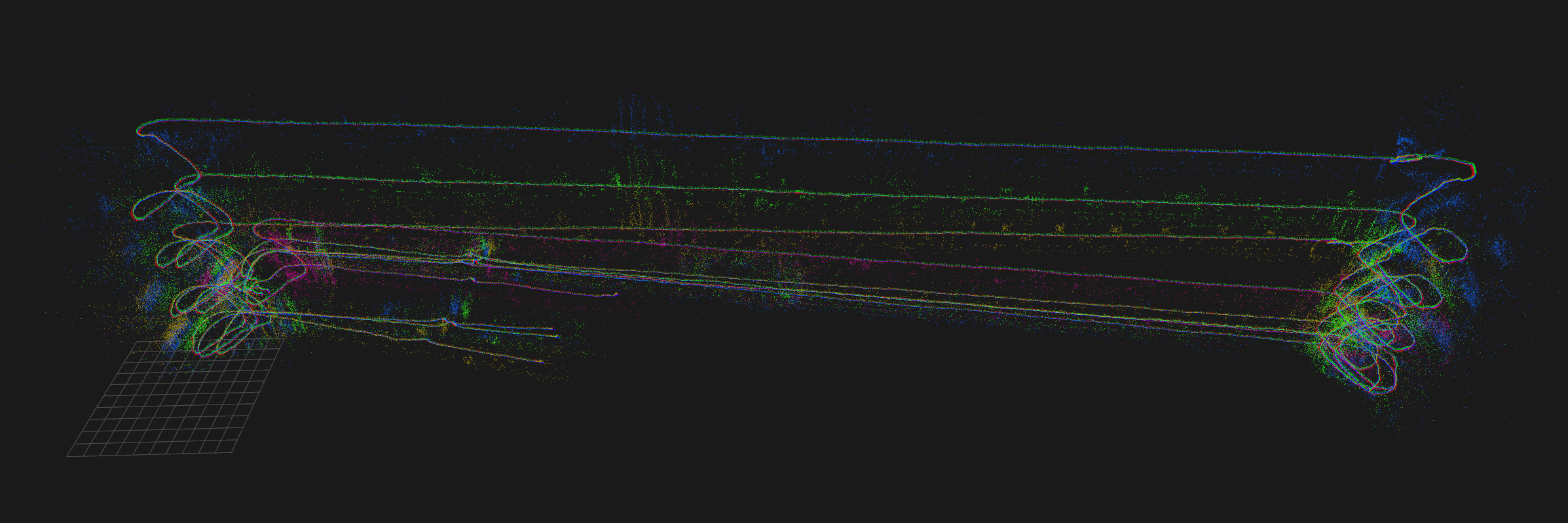
The next step is optional, but will speed up relax, the loop closure and bundle adjustment significantly.
# Key-frame the map. kfhPose-graph relaxation to close large loops:
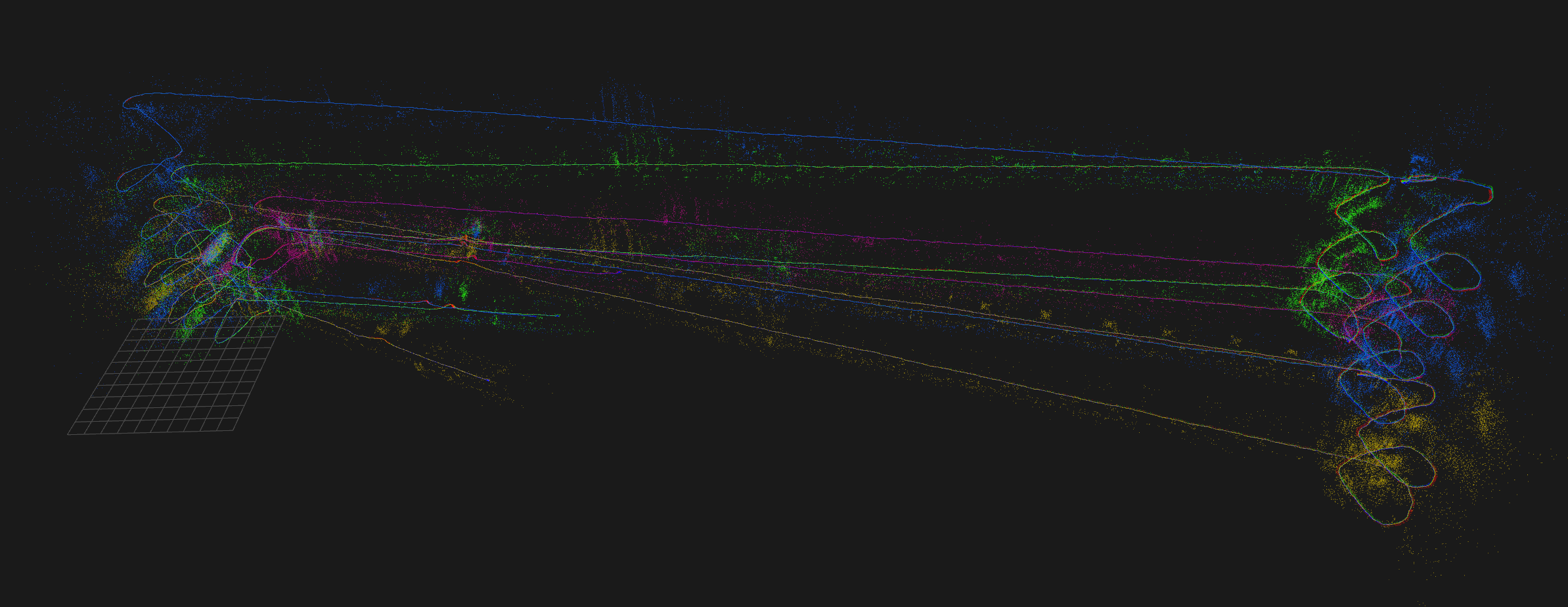
relaxThis should have closed the large loops and aligned the floors:
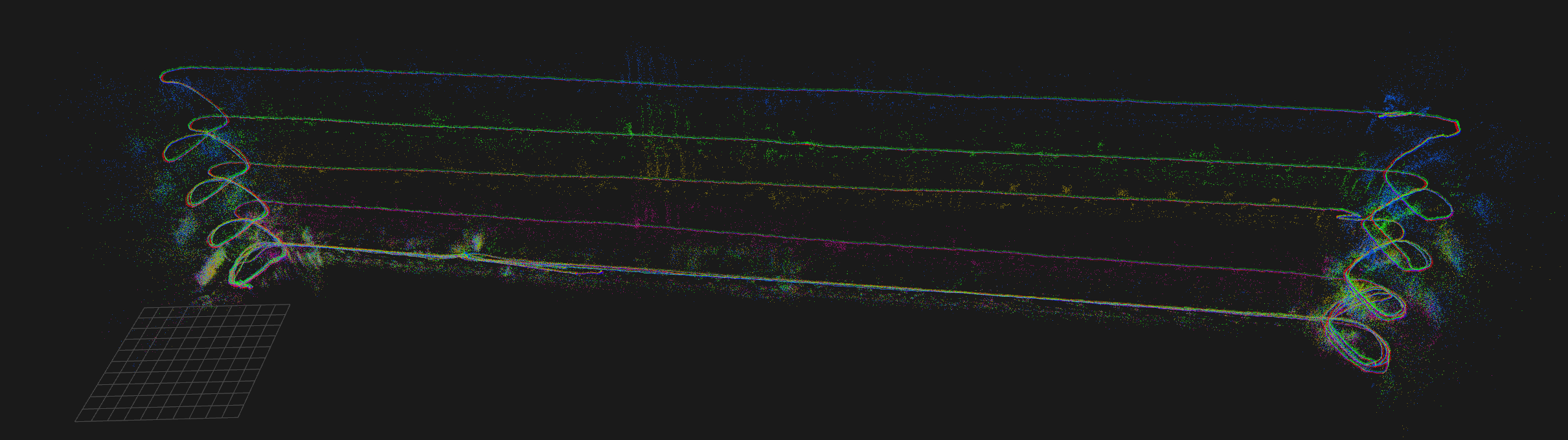
# Loop close the map lc # Bundle adjustment optvi # You can further increase the quality of the map by repeating # lc + optvi or using --ba_num_iterations=50Done: